Airlaid Nonwoven Fabric is widely used in our daily life, But do you know airlaid nonwoven technology and airlaid process? In this article, we’ll talk about what is the process of airlaid nonwoven?

Airlaid is a web formation process. This process is widely used in the production of various products such as sanitary napkins, diapers, and wipes.The process begins with the selection of raw materials. The fibers used in airlaid nonwoven production can be natural or synthetic, such as wood pulp, cotton, rayon, or polyester. The fibers are then mixed with a binder, which can be a thermoplastic material or a water-based adhesive.
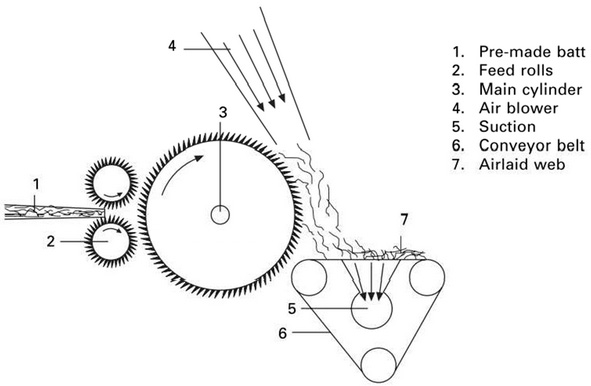
The next step is to form a web of fibers. This can be done through various methods such as air-laying, carding, or wet-laying. In the airlaid nonwoven process, air-laying is the most commonly used method. In this method, the fibers are blown onto a moving belt or drum using a stream of air. The fibers are then bonded together using heat and pressure.
Once the web of fibers is formed, it goes through the bonding process. The bonding process can be done through various methods such as thermal bonding, chemical bonding, or mechanical bonding. Thermal bonding is the most commonly used method in airlaid nonwoven production. In this method, the web of fibers is passed through a heating element that melts the binder and bonds the fibers together.
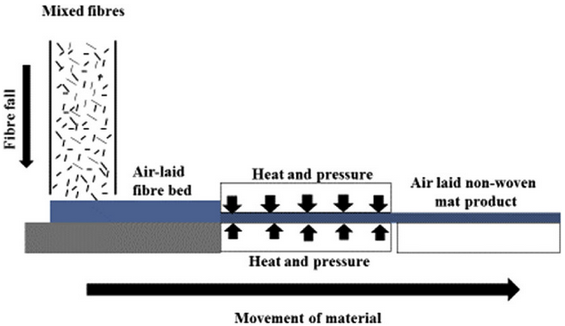
After the bonding process, the web of fibers is then finished. Finishing can include various processes such as cutting, embossing, or laminating. Cutting is used to shape the web of fibers into the desired size and shape. Embossing is used to create a pattern on the surface of the web of fibers. Laminating is used to combine the airlaid nonwoven paper with other materials such as films or foams.
In conclusion, the airlaid nonwoven process is a highly versatile and efficient manufacturing technique that produces a high-quality fiber material with excellent absorbency and softness. This process is widely used in the production of various products, and its use is expected to grow in the future as more industries discover its benefits.
